National Technical Specification Notices
Overview
National Technical Specification Notices (NTSNs) came into effect in Great Britain (GB) on 1 January 2021. These replaced and substantially reproduced the content of the Technical Specifications for Interoperability which apply in the European Union.
NTSNs contain requirements and assessment procedures which must be met to satisfy the ‘essential requirements’ defined in the Railways Interoperability Regulations 2011 (as amended) (RIR). This enables all parts of the railways to run as a whole system.
NTSNs are published by the Secretary of State for Transport on the Department for Transport (DfT) website. They are supplemented by National Technical Rules (NTRs).
-
What do NTSNs cover?
There are 13 NTSNs:
- Eleven cover requirements for subsystems. Each have a corresponding TSI.
- Two cover assessment procedures.
Structural
Control Command and Signalling (CCS)
All trackside and on-board equipment required to command and control movements of trains, including interfaces and compatibility between different systems.
Energy (ENE)
The electrification system, including overhead lines and the trackside of the electricity consumption measuring system.
Infrastructure (INF)
The infrastructure subsystem. For example stations, platforms, tracks, bridges, and tunnels.
Rolling Stock - Locomotive and Passenger (LOC&PAS)
Locomotives and passenger rolling stock requirements. For example the interaction with track, aerodynamic effects, coupling, braking, doors and visible/audible warning devices.
Rolling Stock - Freight Wagons (WAG)
Freight wagon requirements such as compatibility with trackside equipment, running gear, coupling and braking.
Rolling Stock - Noise (NOI)
Requirements for all rolling stock (locomotives, passenger vehicles and freight wagons) to limit noise emissions.
Functional
Operation and Traffic Management (OPE)
The procedures for operation of trains, including train composition and professional qualifications.
Telematics Applications for Passenger Services (TAP)
Applications for passenger services, including systems which provide passengers with information before and during the journey, and reservation and payment systems.
Telematics Applications for Freight (TAF)
Applications for freight services, including allocation systems, payment and invoicing systems, and management of connections with other modes of transport.
Transverse (more than one subsystem)
Accessibility (ACC)
Requirements for persons with reduced mobility for both rolling stock (such as provision for wheelchairs) and stations (such as route identification and facilities).
Safety in Railway Tunnels (SRT)
Requirements to ensure safety in railway tunnels, spanning the infrastructure, energy and rolling stock subsystems.
Assessments
Modules for the procedures for assessment of conformity or suitability for use and UK verification
Replaces Commission Decision 2010/713/EU on ‘modules for the procedures for assessment of conformity, suitability for use and EC verification to be used in the technical specifications for interoperability’
Assessment and further assessment of ICs
Procedures for the assessment of interoperability constituents (ICs) against UK specific cases. This includes the further assessment of ICs which hold an ‘EC’ declaration of conformity or suitability for use.
Further Information
For further information, see resources section of this page. This includes:
- current and previous versions,
- the version of the TSI the NTSN relates to,
- related documents, such as RSSB guidance notes,
- the groups and committees responsible for agreeing recommendations for amendments, and
- an RSSB contact.
Track-changed versions of the NTSNs compared to the corresponding TSI as they applied in January 2021 are also available on request.
-
Who needs to comply with NTSNs?
You must comply with all applicable NTSNs if you are:
- building new railway subsystem, or
- carrying out a major upgrade or renewal of an existing railway subsystem,
and:
- the subsystem is not in the approved list of exclusions from RIR, or
- you do not have an exemption granted by the DfT.
Like-for-like replacements, such as replacing track with track of a similar specification, do not trigger a legal obligation to comply with NTSNs.
You can obtain advice about whether a project must comply with NTSNs from the DfT.
Please note, NTSNs are only applicable in GB; TSIs continue to have effect in Northern Ireland.
For further information, see Complying with legislation and Guidance on the application of railway standards
-
What if i cannot comply with an NTSN?
Changes to NTSNs
The Secretary of State for Transport makes decisions on changes to NTSNs. This includes whether to keep requirements aligned with TSIs. These decisions will consider how best to safeguard the interests of passengers, freight users and the industry.
RSSB manages the process for informing changes to NTSNs. We do this by bringing industry stakeholders together and consulting with them to develop and agree recommendations for changes. Recommendations may be the result of considering TSI changes or proposals from the GB rail industry, so that NTSNs work for the sector.
The DfT wrote to RSSB in September 2023 with a set of policy principles for NTSN revisions (see resources section of this page).
More information on the plans and process for making changes is set out below.
-
How can I request a change to an NTSN?
The first step is to check the NTSN issues log on this page to see if this has already been raised and if the solution resolves your issue.
If not, please submit a Request for Help outlining the problem, the outcome you are seeking and the reasons for this.
Your request will be considered by the relevant mirror group(s), RSSB’s professional heads or technical experts, the relevant standards committee and the DfT to determine the next steps.
-
What is the change process?
The NTSN change process is similar to the process for changes to RSSB’s standards, but with an extra period of DfT decision making. This process is the same whether the change is related to a TSI change or a request from the GB rail industry.
The process is detailed in the Railway Standards Code and Manual and the Working Agreement for the 2023/24 revisions (see resources section of this page).
Firstly, there is initial assessment with the relevant mirror group(s) – which consists of technical experts from across industry – RSSB professional heads, and the DfT to determine whether and how this should be progressed.
Secondly there is a period of assessment led by RSSB and the relevant mirror group(s) to develop a business case for change (BCfC). This sets out initial proposals for development. This is shared with the Industry Standards Coordination Committee (ISCC) and approved by the relevant standards committee(s).
Following standards committee approvals, the BCfC is further developed by RSSB and the mirror group to include the proposed NTSN text and required analysis to support the change. This is provided to the relevant standards committee(s) for approval before wider industry consultation.
Then there is a period of industry consultation to capture any wider challenges or concerns. The responses to consultation and any changes to the NTSN proposals are approved by standards committees as the formal industry recommendation to the DfT.
Once the industry recommendation has been provided to DfT, the process and timing for a decision to publish a revised NTSN depend on the significance of the changes being proposed and scrutiny required. Once the Secretary of State for Transport publishes a revised NTSN, this takes effect.
-
NTSN issues log
The NTSN issues log is available in the resources section of this page.
This is a list of issues we are aware of and proposed solutions. The proposed solution may be a clarification given directly through the issues log, or a change to the NTSN.
Although RSSB manages this log, anyone can raise an issue through a Request for Help.
Maintaining and publishing this issues log helps answer questions that may arise across the sector and track progress against resolving issues.
This log is regularly reviewed by the relevant mirror group(s) and DfT.
-
Latest NTSN revisions
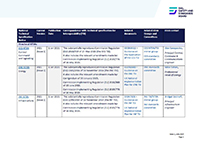
Following publication of revised TSIs in the European Union in September 2023, RSSB issued a formal industry recommendation for revisions to the CCS, INF, LOC&PAS, WAG, NOI, OPE and PRM NTSNs to the DfT on 29 February 2024.
For the revision to the ENE NTSN, industry consensus was not reached, so an RSSB recommendation was made based on the evidence provided through the review and consultation. This was submitted to the DfT on 15 March 2024.
The documents RSSB provided to the DfT are published on our consultation portal. This includes the cover letters accompanying these recommendations, the proposed NTSN text, the business case for change with an assessment and justification of proposals, and the consultation comments and responses.
This revision to the NTSNs was limited to addressing previously known issues and principally to consider changes in the TSIs. However, other important issues have been raised and it is clear that there are many ways these NTSNs can continue to be improved. These revisions are the first step of progressive improvement. We have recorded matters that were not addressed in this revision and work has already commenced on some.
The DfT has published revised NTSNs in May 2025. For questions regarding the application of NTSNs, contact interoperability@dft.gov.uk.
We have prepared resources to understand and identify the differences between NTSN versions. These are:
- A track-checked version showing the differences between the NTSNs published on 2 May 2025 and the previous NTSNs published on 1 January 2021.
- A briefing note for each NTSN providing a high-level overview of the NTSN. This includes its background, what it is about, what has changed from the previous version, the benefits, and who the document is for.
- A business case for change for each NTSN, setting out the industry-recommended revisions to the NTSN and an assessment of the impacts of those revisions.
These are all available in the zip file 'May 2025 NTSN Update pdf's' under Resources below.